IT RISK MANAGEMENT
What is IT Risk Management?
IT Risk Management, also known as Information Security Risk Management, is the process of identifying, assessing, and controlling threats to your organization’s IT infrastructure and data.
It aims to minimize the potential negative impact of those threats and ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of your information systems.
Importance of IT Risk Management?
- Prevent Financial Losses: Proactive identification and mitigation of IT risks can prevent costly incidents like data breaches, downtime, and cyberattacks.
- Lower Insurance Premiums: Demonstrating a strong risk management strategy can lead to lower premiums for cyber insurance and other relevant coverage.
- Improved Resource Allocation: By understanding your IT risks, you can prioritize resources to address the most critical threats, optimizing resource allocation and efficiency.
- Stronger IT Infrastructure: Implementing Risk Management practices strengthens your IT infrastructure, making it more resilient to attacks and vulnerabilities.
- Reduced Compliance Risks: Aligning your IT Controls with relevant regulations minimizes non-compliance fines and penalties.
- Improved Data Protection: Proactive Risk Management safeguards sensitive data, protecting your organization and its customers from privacy breaches.


Importance of IT Risk Management?
- Prevent Financial Losses: Proactive identification and mitigation of IT risks can prevent costly incidents like data breaches, downtime, and cyberattacks.
- Lower Insurance Premiums: Demonstrating a strong risk management strategy can lead to lower premiums for cyber insurance and other relevant coverage.
- Improved Resource Allocation: By understanding your IT risks, you can prioritize resources to address the most critical threats, optimizing resource allocation and efficiency.
- Stronger IT Infrastructure: Implementing Risk Management practices strengthens your IT infrastructure, making it more resilient to attacks and vulnerabilities.
- Reduced Compliance Risks: Aligning your IT Controls with relevant regulations minimizes non-compliance fines and penalties.
- Improved Data Protection: Proactive Risk Management safeguards sensitive data, protecting your organization and its customers from privacy breaches.
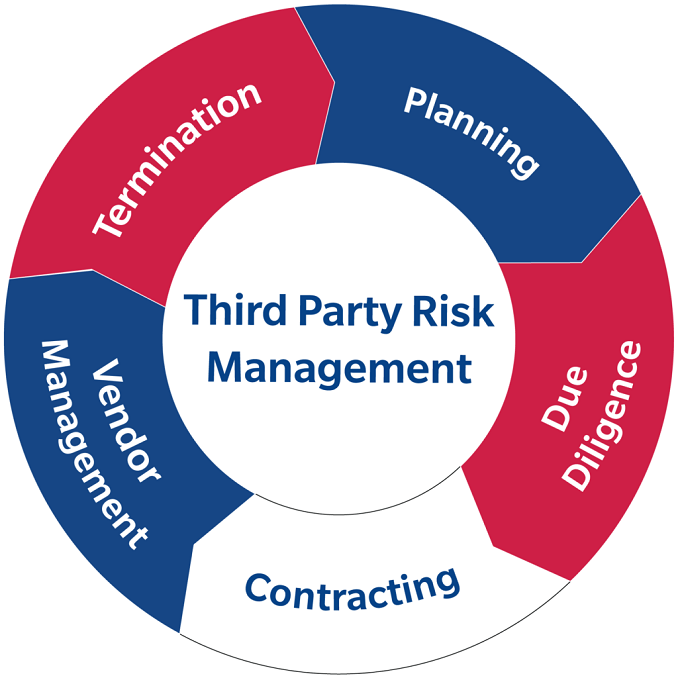
Our Approach
1. Identifying Risks:
- Internal Threats: Considering human error, malicious insiders, system vulnerabilities, and software malfunctions.
- External Threats: Evaluating cyberattacks, data breaches, natural disasters, power outages, and vendor issues.
- Data Sensitivity: Identifying critical data assets and prioritize risks based on potential impact.
2. Analyzing Risks:
- Likelihood: Estimating the probability of each risk occurring based on historical data, industry trends, and threat intelligence.
- Impact: Assessing the potential financial, reputational, and operational consequences if the risk materializes.
- Risk Score: Combining likelihood and impact to prioritize risks requiring immediate attention.
3. Responding to Risks:
- Avoid: Eliminating the risk entirely if possible, like ceasing a vulnerable service or changing data storage practices.
- Mitigate: Reducing the likelihood or impact of the risk through security controls like firewalls, access controls, and data backups.
- Transfer: Sharing the risk with insurance or third-party vendors for specialized expertise.
- Accept: Acknowledging the risk and monitor it closely, especially if avoidance or mitigation proves impractical.
4. Implementing Controls:
- Technical Controls: Installing firewalls, antivirus software, encryption, intrusion detection systems etc.
- Physical Controls: Implementing access controls, security cameras, environmental safeguards etc.
- Administrative Controls: Establishing security policies, procedures, training programs, incident response plans etc.
5. Monitoring and Reviewing:
- Continuous Monitoring: Tracking ongoing threats, system performance, and control effectiveness.
- Conducting Regular Reviews: Reassessing risks regularly, adjusting controls as needed, and adapting to evolving threats and regulations.