PENETRATION TESTING VAPT
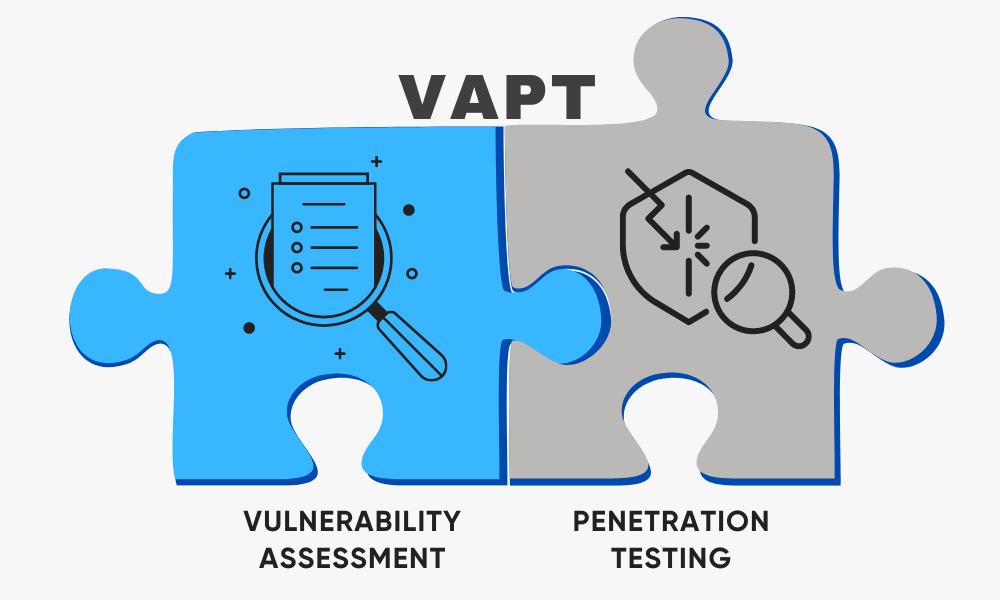
What is VAPT?
VAPT stands for Vulnerability Assessment and Penetration Testing, a powerful approach to identifying and addressing security weaknesses in your network infrastructure, web applications, and other digital assets. Think of it as a deep security scan conducted by ethical hackers to find and fix vulnerabilities before malicious actors can exploit them.
Why does your Organization need to conduct a VAPT?
- Uncover Hidden Vulnerabilities: VAPT goes beyond automated scanners, employing manual penetration testing to discover vulnerabilities missed by automated tools, giving you a more comprehensive understanding of your attack surface.
- Prioritize Remediation Efforts: VAPT reports prioritize vulnerabilities based on their severity, exploitability, and potential impact, allowing you to focus on fixing the most critical issues first.
- Improve Security Maturity: Regular VAPT exercises help you identify and address weaknesses in your security controls and processes, leading to a more mature and resilient security posture over time.
- Proactive Threat Detection: By simulating real-world attacks, VAPT helps you identify potential attack vectors and weaknesses before attackers exploit them, minimizing the risk of data breaches and other security incidents.
- Compliance with Regulations: VAPT can help you demonstrate compliance with industry regulations and data privacy standards, reducing the risk of fines and legal repercussions.
- Build Confidence in Security: Regular VAPT assessments provide valuable insights into your security posture, giving you peace of mind and confidence in your ability to withstand cyberattacks.

Why does your organization need to conduct a VAPT?
- Uncover Hidden Vulnerabilities: VAPT goes beyond automated scanners, employing manual penetration testing to discover vulnerabilities missed by automated tools, giving you a more comprehensive understanding of your attack surface.
- Prioritize Remediation Efforts: VAPT reports prioritize vulnerabilities based on their severity, exploitability, and potential impact, allowing you to focus on fixing the most critical issues first.
- Improve Security Maturity: Regular VAPT exercises help you identify and address weaknesses in your security controls and processes, leading to a more mature and resilient security posture over time.
- Proactive Threat Detection: By simulating real-world attacks, VAPT helps you identify potential attack vectors and weaknesses before attackers exploit them, minimizing the risk of data breaches and other security incidents.
- Compliance with Regulations: VAPT can help you demonstrate compliance with industry regulations and data privacy standards, reducing the risk of fines and legal repercussions.
- Build Confidence in Security: Regular VAPT assessments provide valuable insights into your security posture, giving you peace of mind and confidence in your ability to withstand cyberattacks.
Our Approach
1. Planning & Pre-Engagement:
- Define Scope & Objectives: Clearly define the scope of the VAPT, outlining which systems and applications will be tested. Establish the engagement objectives, such as identifying high-risk vulnerabilities or assessing the effectiveness of existing security controls.
- Information Gathering: The penetration tester gathers information about the target environment, including network diagrams, system configurations, and any relevant security policies. This helps them understand the target system and identify potential attack vectors.
- Threat Modeling: Based on the gathered information, the tester performs threat modeling to identify potential threats and how they might exploit vulnerabilities in the system.
2. Vulnerability Assessment (VA):
- Scanning & Enumeration: The tester uses automated vulnerability scanning tools to identify potential weaknesses in the target system. This might involve scanning for misconfigurations, insecure protocols, and outdated software.
- Manual Testing: The tester complements automated scans with manual penetration testing techniques. This involves exploiting identified vulnerabilities and attempting to gain unauthorized access to the system.
3. Penetration Testing (PT):
- Exploitation: The tester attempts to exploit the identified vulnerabilities using various techniques like social engineering, SQL injection, or password cracking. This helps assess the severity of the vulnerabilities and the potential impact if exploited by a real attacker.
- Post-Exploitation: If the tester successfully gains access to the system, they may attempt to move laterally within the network, escalate privileges, or achieve other objectives defined in the scope. This helps understand the potential damage a real attacker could cause.
4. Reporting & Remediation:
- Findings & Recommendations: The tester documents all identified vulnerabilities, including severity levels, exploitation steps (proof of concept), and recommended remediation actions.
- Post-Penetration Testing Support: The tester might provide guidance on prioritizing vulnerabilities and assist with developing a remediation plan to address the identified weaknesses.
5. Retesting:
- Verification of Remediation: After the identified vulnerabilities are addressed, the tester may perform retesting to verify that the remediation efforts were successful and the vulnerabilities are no longer exploitable.










